You may firmly believe that your staff and customers are the heart and soul of your business, and you’re absolutely right—they are the vital individuals who keep your company running smoothly and ensure its profitability. But have you ever stopped to consider what constitutes the brains behind your organization, such as your data center?
Before you start patting yourself on the back, it’s important to recognize that you might not be the sole answer. Sure, you may be the one steering the ship, making critical decisions, and driving the vision forward, but don’t overlook the significance of your company’s data center—often the true brains behind a successful business. Effective data center capacity planning, coupled with a robust network infrastructure, is crucial. Underestimating these elements can lead to catastrophic consequences, severely impacting your business operations and overall success.

What is a Data Center
If you’re not sure what a data center is, it’s tough to understand its importance to your business. In a nutshell, a data center is a physical space, it can be a room, building, or facility that houses your information technology infrastructure.
Even if you’re using a cloud-based solution, the infrastructure is still in a physical location, which is the infrastructure responsible for creating, running, and delivering services and applications. Your data center also stores and manages the information associated with almost every aspect of your business.
Your business’s data center may be on-premise, in a public cloud, or managed by a third-party supplier. Your organization may use one or more of these types of data centers. Here’s a closer look at the three types of data centers.
On-Premise Data Centers

Also known as enterprise data centers, all of your IT infrastructure is located on-site, which includes your data. You may have a room or an entire building devoted to housing your data center and IT staff, which is the preferred model for companies that want almost complete control over their security protocols.
Having this kind of arrangement can make it easier to comply with the various data security laws like the U.S. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Both of these have rigid data security compliance regulations and violating a standard can result in hefty fines and other penalties.
Generate More Leads With Website & Messenger Chatbots
Gather quality leads on autopilot and 10x your ROI with automated chats
Public Cloud Data Centers
If you don’t want to build a data center for your business or expand an existing one, the public cloud offers scalable solutions. If you have a data-intensive workload running in real-time, the public cloud can maximize efficiency, boost latency, and improve an application’s overall performance.
As we noted, the cloud is also scalable so it can easily handle both small and large workloads as needed. You’re sharing the cloud’s IT infrastructure with other authorized users and this can cause some security concerns.
However, even the public cloud has robust cybersecurity protocols in place to keep your data safe from breaches. Best of all, if a disaster occurs and shuts your network down, your data stays safe in the cloud.
Managed Data Centers

Not every business has the resources to build, house, and manage a data center. While the cloud is always an option, it’s not always the right one for every organization, and this when you can turn to a managed data center.
If you’re not sure what a managed data center is, the simple explanation is you’re leasing the IT infrastructure from a third-party supplier. The third party also handles everything from administration and monitoring to managing the data cente, which can make it a cost-effective solution to use, but it’s also important to work with a reputable and reliable third-party provider.
Components of Data Center Infrastructure
Now that you’re familiar with the various types of data centers, it’s time to look at the infrastructure. These are the components that make up a fully functional data center.
Data Center Servers
Your servers are computers that send data, services, and applications to users’ devices. An example is if an employee downloads an application to a personal computer, the information is sent from the server.
Data centers can use either rack-mounted, blade, or mainframe servers. Which is best for a business depends on multiple factors like available power, workloads, and data center space.
Data Center Storage Systems
Your servers have some storage capacity but it’s usually not enough. To ensure data isn’t getting lost, data centers install storage systems near the central processing units (CPUs).
You have a few options when it comes to the type of storage system. You can use direct-attached storage DAS), network-attached storage (NAS), or a storage area network (SAN). DAS is the most commonly used storage system, but both NAS and SAN also have advantages. Some data centers use all three types of storage systems to help ensure their data is always accessible.
Data Center Networking

Without networking, a data center is simply a collection of servers and other systems. Your networking consists of routers, switches, and fiber optics to deliver network traffic across the data center’s servers.
Your networking can be physical or virtual. The option that’s best for you typically depends on your business needs. Your budget can also play a role in your network configuration.
Power Supply and Cable Management In Data Center
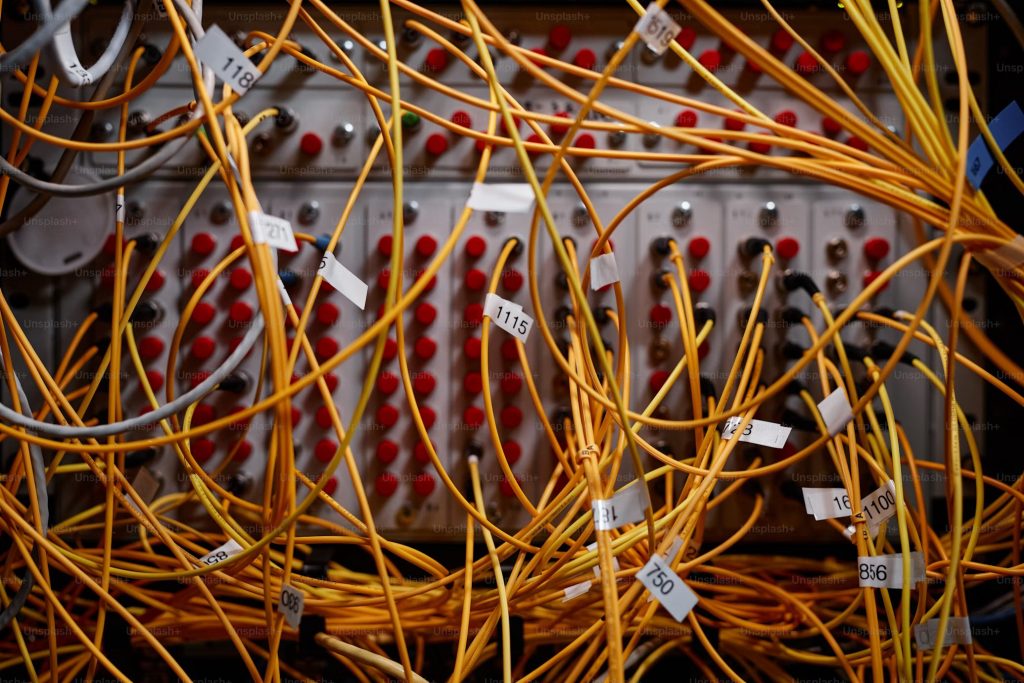
If your data center goes dark, there’s an issue. The power should always be on, even when your business is closed. If you’re not already using a dual power supply, now’s a good time to get started. A dual power supply typically includes electricity combined with other energy sources like batteries and solar.
Cable management is also something you don’t want to overlook. Most data centers have multiple cables connecting servers and other components to each other and power supplies. If you’re not managing your cables, you can run into problems with heat management and slower data transfer rates. Even signal transmission can be negatively affected if your cables are too close to each other.
Your Data Center Runs Your Business
Managing data centers is often a complex task to undertake, even for smaller businesses. Whether your data center is on-site, in the cloud, or managed by a third-party provider, it plays a fundamental role in running your business.
No matter which option you choose, it’s essential to make sure that your infrastructure can effectively deliver services and applications to both your staff and customers. Having the right setup in place is key to maintaining smooth operations and meeting the demands of your organization.
Are You Ready To SkyRocket Your Business With Our AI Chatbots
Click The Button Below And Gather Quality Leads With Botsify

